Monday, July 29, 2013
Antialiasing And Sync Compensation Filter Circuit Diagram
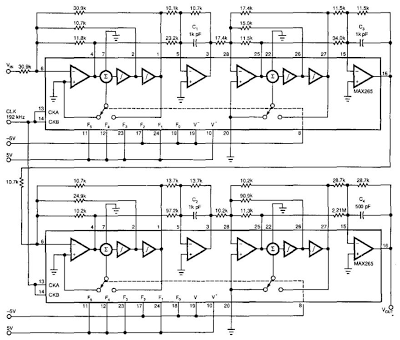
Antialiasing And Sync-Compensation Filter Circuit Diagram. Two dual-bi-quad filter chips and some external components form a multipurpose filter to reconstruct D/A converter signals. Connected to a converter`s output, the filter provides anti-aliasing, reduces the D/A converter`s quantization noise, and compensates for sin(7rx)()—the `sync` function (attenuation). The circuit incorporates an inverse-sync function that operates to one-third of the converter`s sample rate. Beyond one-third, the filter`s response shifts to a stop band filter, which provides -70 dB attenuation.
This attenuation conforms to the converter`s inherent signal-to-noise ratio and quantization error. To prevent aliasing, the stop band edge must be no higher than the Nyquist frequency (/„ + 2). To achieve 70-dB stop band rejection with this eighth-order filter requires a transition ratio (/stop band -K/pass band) of 1.5, which sets the passband`s upper limit at fs +3. Notice also that you can apply a simple divide-by-64 circuit to the 192-kHz clock frequency to set the necessary 3 ratio between the converter`s sample rate and the filter`s 1-kHz corner frequency.
Antialiasing And Sync-Compensation Filter Circuit Diagram
Labels:
and,
antialiasing,
circuit,
compensation,
diagram,
filter,
sync