Showing posts with label ic. Show all posts
Showing posts with label ic. Show all posts
Wednesday, July 31, 2013
IC 555 Design Note
The popular Timer IC 555 is extensively used in short duration timing applications. IC 555 is a highly stable integrated circuit functioning as an accurate time delay generator and free running multivibrator. But one of the serious problem in 555 timer design is the false triggering of the circuit at power on or when voltage changes. The article describes how IC555 is designed perfectly to avoid false triggering.
555 IC pin functions
Pin1 Ground
Pin2 Trigger
Pin3 Output
Pin 4 Reset
Pin 5 Control voltage
Pin 6 Threshold
Pin 7 Discharge
Pin 8 Vcc
Functional aspects of pins
Trigger Pin 2
Usually pin2 of the IC is held high by a pull up resistor connected to Vcc. When a negative going pulse is applied to pin 2, the potential at pin 2 falls below 1/3 Vcc and the flip-flop switches on. This starts the timing cycle using the resistor and capacitor connected to pins 6 and 7.
Reset pin 4
Reset pin 4 can be controlled to reset the timing cycle. If pin 4 is grounded, IC will not be triggered. When pin4 becomes positive, IC becomes ready to start the timing cycle. Reset voltage is typically 0.7 volts and reset current 0.1 mA. In timer applications, reset pin should be connected to Vcc to get more than 0.7 volts.
Control Voltage pin 5
Pin5 can be used to control the working of IC by providing a DC voltage at pin5. This permits the control of the timing cycle manually or electronically. In monostable operation, the control pin5 is connected to ground through a 0.01 uF capacitor. This prevents the timing interval from being affected by AC or RF interference. In the Astable mode, by applying a variable DC voltage at pin 5 can change the output pulses to FM or PWM.
Threshold pin 6 and Discharge pin 7
These two inputs are used to connect the timing components- Resistor and Capacitor. The threshold comparator inside the IC is referenced at 2/3 Vcc and the trigger comparator is referenced at 1/3 Vcc. These two comparators control the internal Flip-Flop of the circuit to give High or Low output at pin 3.When a negative going pulse is applied to pin 2, the potential at pin2 drops below 1/3 Vcc and the trigger comparator switches on the Flip-Flop. This turns the output high. The timing comparator then charges through the timing resistor and the voltage in the timing capacitor increases to 2/3 Vcc.( The time delay depends on the value of the resistor and capacitor.
That is, higher values, higher time).When the voltage level in the capacitor increases above 2/3 Vcc, the threshold comparator resets the Flip-Flop and the output turns low. Capacitor then discharges through pin 7.Once triggered, the IC will not responds to further triggering until the timing cycle is completed. The time delay period is calculated using the formula T= 1.1 Ct Rt. Where Ct is the value of Capacitor in PF and Rt is the value of Resistor in Ohms. Time is in Seconds.
How to eliminate false triggering?
The circuit diagram shown below is the simple monostable using IC 555. To eliminate the false triggering resistor R1 and Capacitor C1 are connected to the reset pin 4 of the IC. So the reset pin is always high even if the supply voltage changes. Moreover capacitor C3 connected close to the Vcc pin 8 acts as a buffer to maintain stable supply voltage to pin 8. Using this design, it is easy to avoid false triggering to a certain extent.
555 IC pin functions
Pin1 Ground
Pin2 Trigger
Pin3 Output
Pin 4 Reset
Pin 5 Control voltage
Pin 6 Threshold
Pin 7 Discharge
Pin 8 Vcc
Functional aspects of pins
Trigger Pin 2
Usually pin2 of the IC is held high by a pull up resistor connected to Vcc. When a negative going pulse is applied to pin 2, the potential at pin 2 falls below 1/3 Vcc and the flip-flop switches on. This starts the timing cycle using the resistor and capacitor connected to pins 6 and 7.
Reset pin 4
Reset pin 4 can be controlled to reset the timing cycle. If pin 4 is grounded, IC will not be triggered. When pin4 becomes positive, IC becomes ready to start the timing cycle. Reset voltage is typically 0.7 volts and reset current 0.1 mA. In timer applications, reset pin should be connected to Vcc to get more than 0.7 volts.
Control Voltage pin 5
Pin5 can be used to control the working of IC by providing a DC voltage at pin5. This permits the control of the timing cycle manually or electronically. In monostable operation, the control pin5 is connected to ground through a 0.01 uF capacitor. This prevents the timing interval from being affected by AC or RF interference. In the Astable mode, by applying a variable DC voltage at pin 5 can change the output pulses to FM or PWM.
Threshold pin 6 and Discharge pin 7
These two inputs are used to connect the timing components- Resistor and Capacitor. The threshold comparator inside the IC is referenced at 2/3 Vcc and the trigger comparator is referenced at 1/3 Vcc. These two comparators control the internal Flip-Flop of the circuit to give High or Low output at pin 3.When a negative going pulse is applied to pin 2, the potential at pin2 drops below 1/3 Vcc and the trigger comparator switches on the Flip-Flop. This turns the output high. The timing comparator then charges through the timing resistor and the voltage in the timing capacitor increases to 2/3 Vcc.( The time delay depends on the value of the resistor and capacitor.
That is, higher values, higher time).When the voltage level in the capacitor increases above 2/3 Vcc, the threshold comparator resets the Flip-Flop and the output turns low. Capacitor then discharges through pin 7.Once triggered, the IC will not responds to further triggering until the timing cycle is completed. The time delay period is calculated using the formula T= 1.1 Ct Rt. Where Ct is the value of Capacitor in PF and Rt is the value of Resistor in Ohms. Time is in Seconds.
How to eliminate false triggering?
The circuit diagram shown below is the simple monostable using IC 555. To eliminate the false triggering resistor R1 and Capacitor C1 are connected to the reset pin 4 of the IC. So the reset pin is always high even if the supply voltage changes. Moreover capacitor C3 connected close to the Vcc pin 8 acts as a buffer to maintain stable supply voltage to pin 8. Using this design, it is easy to avoid false triggering to a certain extent.
555 Monostable circuit

A ready recknor to select timing resistor and capacitor

Theoretically long interval is possible with IC 555,but in practical conditions, it is difficult to get more than 3 minutes. If low leakage Tantalum capacitor is used, this can be increased to 5 minutes or more. If the value of the timing capacitor is too high above 470 uF, charging time will be prolonged which will upset the timing cycle and the output remains high even after the desired time is over.
Streampowers
Wednesday, May 1, 2013
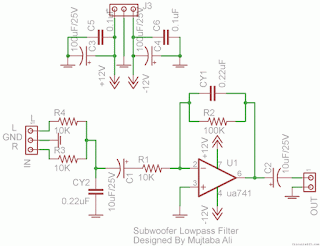
Simple Subwoofer Lowpass Filter using uA741 Single Op Amp Ic
This is the simplest Sub woofer Low Pass filter Circuit using uA741 single op amp ic. The circuit is very low cost with respect to their work. The cut off frequency of this circuit is 25Hz to 80Hz maximum. Using this circuit , you can easily design a 2.1 Sub-woofer Speaker System at your own Home. The circuit contains very few components.In Pakistan, the cost of this circuit with PCB is Rs:45 The same circuit is working in my own hand made sub-woofer system.
R1,R3,R4 = 10K 1/4W
R2=100K 1/4W
CY1,CY2 = 0.22uF Polyester
C1,C2 = 10uF/25V Electrolytic
IC1 = uA741A Single Op-Amp Ic + 8 Pin Ic Socket
3 Pin Male & Female Connector x 2
2 Pin Male & Female Connector x 1
PCB as in required size 4.5 cm x 3.4 cm
Friday, April 12, 2013
Sound Shifter Using IC HT8950
This is a design circuit for super sound shifter circuit that can be used to add effects to the input sound signal. The circuit is ideal for incorporating in toys and adds great fun. The circuit can be also used in mixers and recorders. The circuit is based on IC HT 8950 from Holtek. The IC HT8905 is a single chip CMOS sound modulator IC which produces seven steps of shift in the frequency of the given sound. This is the complete figure of the circuit.

This circuit is producing a dramatic change in the output. The IC produces two effects robotic and vibrato. The two effects can be selected using push buttons. An audio amplifier IC HT82V 733 is also included in the circuit to amplify the sound out put of HT 8950 to a reasonable level. The 50 K POT can be used as a volume control. The circuit can be powered from a 4.5 V DC supply. The desired sound effects can be selected from the push buttons. All capacitors must be rated 10V. For speaker is using 8 ohm speaker can be used as the load.

This circuit is producing a dramatic change in the output. The IC produces two effects robotic and vibrato. The two effects can be selected using push buttons. An audio amplifier IC HT82V 733 is also included in the circuit to amplify the sound out put of HT 8950 to a reasonable level. The 50 K POT can be used as a volume control. The circuit can be powered from a 4.5 V DC supply. The desired sound effects can be selected from the push buttons. All capacitors must be rated 10V. For speaker is using 8 ohm speaker can be used as the load.
Tuesday, April 9, 2013
IC LM 386 Datasheet Explained in Simple Words
The IC LM386 is a 8-pin tiny power amplifier chip, specially made for operating under relatively low voltage parameters, yet provide considerable amplification. It becomes suitable for applying in small low power audio gadgets like in FM radios, door bells, telephones etc.
Lets begin the IC LM386 datasheet explanation by studying its absolute maximum ratings first, meaning the parameters which should not be exceeded while using this IC in any circuit:
Supply Voltage: Max. 15V (Typical)
Input Voltage: +/- 0.4 volts
Storage Temperature: -65 degrees to +150degrees Celsius
Operating Temperature: 0 to 70 degrees Celsius
Power Output: 1.25 watts
IC manufactured by:

How to Control Gain for the IC LM386
In order to make the IC better with its response, its pin#1 and 8 have been attributed with a gain control facility which may be set externally.
Gain simply means the capacity or the amplifying level of the device up to which it is able to amplify the applied input low signal audio input.
When the above pin outs are kept unconnected to anything, the internal 1.35K resistor sets the gain of the IC to 20.
If a capacitor is joined across the above pin outs, the gain is suddenly lifted to 200.
The gain may be simply made adjustable by connecting a pot in series with the above explained capacitor across the pin 1 and 8.
Practical Amplifier Circuit Diagrams Using the IC LM386
The following figure shows a typical LM386 amplifier circuit having the bare minimum number of components required to make the IC operate at its internally set level of gain 20.
The speaker used is a 2 watt, 8 Ohms type.
The input at Vin may be fed from any audio source such as a cell phone headphone socket, a CD/DVD player RCA L or R socket or any other similar source.
The pin Vs should be connected to +12V DC supply from an AC DC adapter or a home made transformer/bridge power supply unit.
Pin #4 should be connected to ground or the negative of the power supply.
The earth wire or the negative wire from the input audio source should also be connected to the above negative of the power supply.

The input pin#2 goes to a 10K pot which becomes the volume control, one of its end terminals is picked for receiving the input signal while the other end is connected to ground, the center one goes to the hot end of the IC.
The speaker is connected to in #8 via a high value blocking capacitor, the resistor/capacitor arrangement connected across pin #5 and ground has been included for frequency compensation and to provide greater stability to the circuit.
The next circuit shows a similar design as above, except that its pins 1 and 8 have been connected to a capacitor of 10uF, which as explained above helps to pull the gain of the amplifier to 200

Lets begin the IC LM386 datasheet explanation by studying its absolute maximum ratings first, meaning the parameters which should not be exceeded while using this IC in any circuit:
Supply Voltage: Max. 15V (Typical)
Input Voltage: +/- 0.4 volts
Storage Temperature: -65 degrees to +150degrees Celsius
Operating Temperature: 0 to 70 degrees Celsius
Power Output: 1.25 watts
IC manufactured by:
How to Control Gain for the IC LM386
In order to make the IC better with its response, its pin#1 and 8 have been attributed with a gain control facility which may be set externally.
Gain simply means the capacity or the amplifying level of the device up to which it is able to amplify the applied input low signal audio input.
When the above pin outs are kept unconnected to anything, the internal 1.35K resistor sets the gain of the IC to 20.
If a capacitor is joined across the above pin outs, the gain is suddenly lifted to 200.
The gain may be simply made adjustable by connecting a pot in series with the above explained capacitor across the pin 1 and 8.
Practical Amplifier Circuit Diagrams Using the IC LM386
The following figure shows a typical LM386 amplifier circuit having the bare minimum number of components required to make the IC operate at its internally set level of gain 20.
The speaker used is a 2 watt, 8 Ohms type.
The input at Vin may be fed from any audio source such as a cell phone headphone socket, a CD/DVD player RCA L or R socket or any other similar source.
The pin Vs should be connected to +12V DC supply from an AC DC adapter or a home made transformer/bridge power supply unit.
Pin #4 should be connected to ground or the negative of the power supply.
The earth wire or the negative wire from the input audio source should also be connected to the above negative of the power supply.

The input pin#2 goes to a 10K pot which becomes the volume control, one of its end terminals is picked for receiving the input signal while the other end is connected to ground, the center one goes to the hot end of the IC.
The speaker is connected to in #8 via a high value blocking capacitor, the resistor/capacitor arrangement connected across pin #5 and ground has been included for frequency compensation and to provide greater stability to the circuit.
The next circuit shows a similar design as above, except that its pins 1 and 8 have been connected to a capacitor of 10uF, which as explained above helps to pull the gain of the amplifier to 200

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)